Having a website is essential for building an online presence, but simply creating content isn’t enough to secure a top spot on Google’s search results. If your web pages aren’t ranking, it can be frustrating and might even impact your business’s visibility, traffic, and growth. Understanding why your content isn’t appearing in search results is crucial to addressing the problem and boosting your site’s search engine optimization (SEO) performance.
Several factors can prevent your web pages from ranking on Google. These can range from technical SEO problems, like slow loading times and poor mobile compatibility, to content-related issues such as keyword cannibalization and unoptimized content. Problems with indexing, crawlability, backlinks, or even Google penalties due to algorithm updates can also affect your site’s position in search results.
This guide breaks down 16 common reasons why your page may not be ranking on Google and provides practical solutions for each issue. Let’s dive into each potential problem and explore how to address it effectively.
Indexing and Crawlability Issues
Ensuring your site is properly indexed and crawled by Google is a fundamental step in SEO. If search engines can’t access your pages or understand their content, your site won’t appear in search results. Here are some common issues related to indexing and crawlability that could be hindering your page’s ranking on Google.
1. Your Website/Page Is New
When a website or a specific page is newly launched, it might take some time for search engines to find and index it. Google uses web crawlers to discover content across the internet, but it doesn’t happen instantaneously, especially for new sites with low authority. If your website is fresh, it might not have been crawled yet, or it could be sitting in a queue waiting to be indexed.
The Solution
To help Google find and index your new website, create a sitemap, which is a file that lists all the URLs on your site, helping search engines understand its structure. Once the sitemap is ready, submit it to Google to speed up the indexing process.
How Do I Create a Sitemap?
Creating a sitemap is relatively easy:
- If you’re using a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, plugins such as Yoast SEO or All in One SEO can automatically generate a sitemap for you.
- For other platforms, you can manually create a sitemap using tools like XML-Sitemaps.com or Screaming Frog.
The sitemap should be in an XML format to be compatible with search engines.
How Do I Submit My Sitemap to Google?
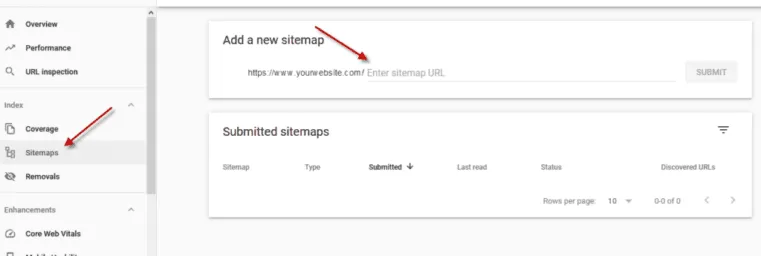
After creating a sitemap, follow these steps to submit it to Google:
- Sign in to Google Search Console.
- In the left-hand menu, select “Sitemaps.”
- Enter your sitemap’s URL in the “Add a new sitemap” field, then click “Submit.”
- Google will then process the sitemap and start crawling your website.
Submitting a sitemap not only helps Google index your site but also notifies the search engine whenever new content is added.
2. Your Content/Site Is Marked ‘noindex’
A “noindex” tag is an HTML meta tag used to prevent specific pages from appearing in search results. It can be helpful for private or duplicate content that you don’t want to be indexed. However, if your important pages or entire site are accidentally marked “noindex,” Google will not display them in search results, regardless of their quality.
How Can I Check if My Site Has a ‘noindex’ Tag?
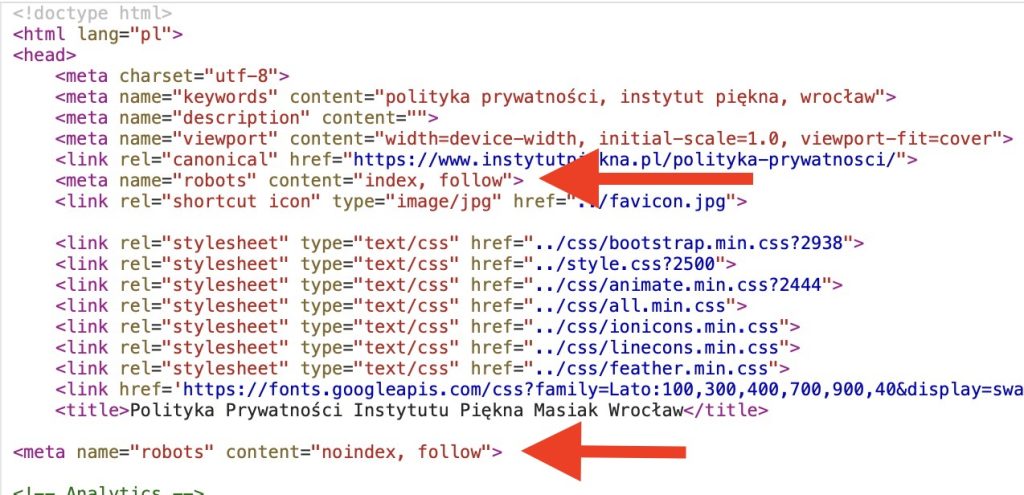
To check if your site or certain pages are marked “noindex”:
- View the page source code by right-clicking on the webpage and selecting “View Page Source.”
- Look for the
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">tag. If this tag is present, the page is set to “noindex.”
Alternatively, you can use SEO tools like Screaming Frog or SEMrush to crawl your website and detect any “noindex” tags.
The Solution
If you find “noindex” tags on important pages:
- Remove the
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">tag from the HTML source code. - If using WordPress, navigate to the page or post settings and ensure the “Discourage search engines from indexing this site” option is unchecked in the “Reading” settings.
- Resubmit the affected URLs to Google through Google Search Console by navigating to “URL Inspection” and requesting indexing.
Once the “noindex” tag is removed, Google will be able to crawl and potentially rank your page.
3. Your Site Is Blocking Google With a robots.txt File
The robots.txt file is used to instruct search engines on which parts of a website should not be crawled. While this file is useful for keeping private or non-essential content from being indexed, misconfigurations can block important sections of your site from being crawled by Google. If the robots.txt file is set up incorrectly, it could be telling search engines to ignore your entire site or crucial pages.
How Do I Check if My robots.txt File Is Blocking Googlebot?
To check your robots.txt file:
- Go to your website’s URL and add
/robots.txtat the end (e.g.,www.yoursite.com/robots.txt). - Look for any lines that include
User-agent: *followed byDisallow: /, which would indicate that all pages are being blocked from crawling. - Ensure there are no lines like
Disallow: /important-page/if you want that page to be indexed.
You can also use Google Search Console’s “robots.txt Tester” tool to identify any issues with your robots.txt file.
The Solution
If your robots.txt file is blocking important content:
- Edit the file to remove or adjust any “Disallow” directives that are preventing Googlebot from crawling valuable pages.
- For example, replace
Disallow: /(which blocks the entire site) with more specific entries, likeDisallow: /private-section/if you only want certain sections hidden. - After making changes, test the new configuration using Google Search Console’s “robots.txt Tester” to confirm that your adjustments allow Google to crawl the correct parts of your site.
Ensuring your robots.txt file is properly configured can help restore Google’s ability to crawl and index your site, improving its chances of ranking.
Technical SEO Problems
Technical SEO issues can severely affect your website’s ability to rank well on Google. Ensuring that your site is optimized from a technical standpoint can improve its search visibility, user experience, and overall performance. Let’s look at some common technical SEO problems that could be preventing your page from ranking and how to resolve them.
4. Your Page Has Long Loading Times (Page Speed)
Page speed is a crucial factor in SEO, as slow-loading pages can negatively impact user experience and result in higher bounce rates. If your website takes too long to load, Google may perceive it as offering a poor user experience, which can hurt your rankings.
How Do I Check My Page Speed?
To check your page speed:
- Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, which analyzes your page’s performance on both mobile and desktop devices and provides recommendations for improvement.
- GTmetrix and Pingdom are also useful tools for evaluating page speed and getting detailed insights into load times, performance scores, and specific areas that need attention.
These tools will give you a breakdown of the factors affecting your page speed, such as image sizes, server response times, and unnecessary scripts.
The Solution
Improving your page speed involves optimizing various aspects of your website:
- Optimize images: Compress large images to reduce their file size without compromising quality. Tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim can help.
- Minimize HTTP requests: Reduce the number of elements on your page that require separate server requests, such as scripts, images, and stylesheets.
- Enable browser caching: This allows returning visitors to load your page faster by storing certain data locally.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): CDNs distribute your content across multiple servers worldwide, enabling faster delivery based on the user’s location.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Remove unnecessary code to reduce file size and improve load times.
- Upgrade your hosting: If your current server is slow, consider switching to a better hosting plan or provider.
5. Your Site Isn’t Mobile-Friendly
With the increasing number of users accessing websites from mobile devices, having a mobile-friendly website is essential. Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of your website for ranking and indexing. If your site isn’t optimized for mobile, it could suffer in search rankings.
How Can I Check if My Website Is Mobile-Friendly?
To check if your site is mobile-friendly:
- Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool (https://search.google.com/test/mobile-friendly) to analyze individual pages.
- Google Search Console also offers a “Mobile Usability” report that highlights any mobile usability issues across your site.
These tools will indicate whether your site is mobile-friendly and identify any specific issues, such as text that’s too small to read or elements that are too close together.
The Solution
To ensure your website is mobile-friendly:
- Use a responsive design: Make sure your website layout adjusts smoothly to different screen sizes and orientations.
- Optimize navigation for mobile users: Use a simplified menu structure and make buttons large enough for users to tap easily.
- Avoid using Flash or other outdated technologies: These can negatively impact mobile usability.
- Test your site on various devices and browsers: Make sure the user experience is consistent across different mobile platforms.
- Improve mobile page speed: Follow the steps mentioned in the previous section to ensure your site loads quickly on mobile devices.
Addressing mobile-friendliness is not just about ranking higher on Google; it’s also about delivering a positive experience to users, regardless of how they access your website.
6. You’re Being Penalized Because You Went Against Webmaster Guidelines
Google’s Webmaster Guidelines outline the best practices for building and maintaining a site that complies with search engine standards. If your site engages in manipulative practices or violates these guidelines, it could face manual or algorithmic penalties, causing a drop in rankings.
How Can I Check if My Site Is Violating Webmaster Guidelines?
To check if your site has been penalized:
- Google Search Console provides a “Manual Actions” report, which indicates if your site has any manual penalties. This section will outline the specific reasons for the penalty and suggest actions to resolve the issue.
- Additionally, keep an eye on your site’s performance. A sudden and significant drop in organic traffic could indicate an algorithmic penalty, often related to recent updates in Google’s search algorithms.
The Solution
If you discover your site has been penalized:
- Identify and resolve the issue: Review the reason for the penalty and take corrective action. Common violations include keyword stuffing, cloaking, or having thin or low-quality content.
- Submit a reconsideration request: After fixing the issues, use Google Search Console to submit a request explaining the steps you’ve taken to comply with the guidelines.
- Avoid future violations: Regularly review Google’s Webmaster Guidelines to stay updated on best practices and avoid tactics that could result in penalties.
Following Google’s guidelines is critical for maintaining your website’s search visibility and preventing ranking drops due to penalties.
7. Your Website Has Security Issues
Security is a significant factor in Google’s ranking algorithm. Websites with security vulnerabilities, such as malware or lacking HTTPS encryption, may be flagged as unsafe, leading to lower rankings or even removal from search results.
How Do I Check if My Website Has Security Issues?
To check for security issues:
- Google Search Console provides a “Security Issues” report, indicating if your site has been compromised or has other security-related problems.
- Google’s Safe Browsing tool can also be used to check if your site is marked as unsafe.
- Use a website security scanner, such as Sucuri SiteCheck or Qualys SSL Labs, to perform a comprehensive security assessment.
The Solution
If your website has security issues, take the following steps:
- Switch to HTTPS: Ensure your site is using a secure connection by obtaining an SSL certificate and switching from HTTP to HTTPS.
- Remove malware or malicious content: If your site is hacked or contains malware, clean up the affected files and update all passwords. You may need to work with a security expert to fix any vulnerabilities.
- Regularly update software and plugins: Keep your CMS, themes, and plugins updated to the latest versions to avoid potential security exploits.
- Implement strong security practices: Use firewalls, malware detection tools, and regular security audits to maintain your site’s integrity.
By addressing security concerns, you not only improve your chances of ranking better on Google but also ensure a safer browsing experience for your users.
Link Building and Backlinking Issues
Link building and the quality of your backlinks play a crucial role in your site’s SEO. A strong backlink profile can significantly boost your rankings, while poor-quality or broken links can hurt your SEO efforts. Let’s explore some common backlink-related issues that might be preventing your page from ranking well on Google.
8. Your Site Has Broken or Toxic Backlinks
Backlinks from reputable sites signal to search engines that your content is valuable and trustworthy. However, if your site has broken or toxic backlinks, it can negatively impact your ranking. Broken backlinks are links that lead to non-existent or deleted pages, while toxic backlinks come from spammy or low-quality websites.
How Do I Check if My Site Has Broken or Toxic Backlinks?
To identify broken or toxic backlinks:
- Use tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to conduct a backlink analysis. These tools will allow you to see which websites are linking to your site and highlight any broken or potentially harmful links.
- Google Search Console can also be used to identify broken links by checking for crawl errors and examining your site’s backlink profile.
- Monitor for sudden spikes in backlinks: A rapid increase in low-quality backlinks can indicate a negative SEO attack or spammy link-building tactics.
The Solution
To fix broken or toxic backlinks:
- Remove or disavow toxic backlinks: Contact webmasters of low-quality sites linking to your page and request link removal. If removal is not possible, use the Google Disavow Tool to inform Google that you do not want these links to affect your site.
- Fix broken backlinks: If the broken links are from your site, update or redirect them to relevant and existing pages. If the broken links are coming from external sites, consider reaching out to the webmasters to update their links.
- Monitor your backlink profile regularly: Regularly use backlink analysis tools to detect and address any harmful backlinks before they impact your ranking.
Maintaining a clean and healthy backlink profile is essential for improving your search engine visibility and avoiding penalties.
9. Your Site Is Not Getting Enough Quality Backlinks
Backlinks from authoritative and relevant sites are critical to your SEO success. If your website lacks sufficient high-quality backlinks, it may struggle to rank for competitive keywords.
How Do I Check the Quality of My Website’s Backlinks?
To assess your backlink quality:
- Use tools like Ahrefs, Moz, or SEMrush to check the “Domain Authority” (DA) or “Domain Rating” (DR) of the sites linking to you. Higher DA/DR scores indicate stronger and more valuable backlinks.
- Look for relevance: Ensure the linking sites are relevant to your industry or niche, as search engines give more weight to relevant backlinks.
- Analyze anchor text: Make sure the anchor text used in backlinks is diverse and not overly optimized for specific keywords.
The Solution
To acquire more quality backlinks:
- Create high-quality content: Publish valuable and shareable content, such as blog posts, infographics, or original research, to encourage other sites to link to you.
- Engage in guest blogging: Write guest posts for reputable websites in your niche, which can help you earn quality backlinks.
- Use broken link building: Find broken links on other websites and suggest your content as a replacement, providing value to the site owner and gaining a backlink.
- Leverage social media and content promotion: Share your content on social media platforms and forums to increase its visibility and the likelihood of earning backlinks.
Acquiring high-quality backlinks can significantly enhance your site’s authority and improve its chances of ranking on search engines.
10. Your Site Has a Poor Internal Linking Structure
Internal linking helps search engines understand the structure of your website and distribute link equity across different pages. If your site has a poor internal linking structure, search engines may struggle to index your pages effectively, which can hinder your SEO efforts.
The Solution
To improve your internal linking structure:
- Use descriptive anchor text: Ensure the anchor text used in internal links is relevant and descriptive, indicating the content of the linked page.
- Link to important pages from high-traffic pages: If some of your pages receive more traffic than others, link them to important but less visited pages to spread link equity.
- Create topic clusters: Organize your content around main topics and link related articles to one another, reinforcing the topical relevance.
- Avoid excessive linking: While internal linking is beneficial, overloading a page with too many links can dilute link value and confuse search engines.
Improving your internal linking structure ensures that search engines can easily crawl and index your site, making it easier to rank for relevant keywords.
Content and Keyword-Related Issues
Content quality and keyword usage play an essential role in determining your website’s visibility on search engines. Several common content-related issues can prevent your pages from ranking well. Let’s look at some of these problems and how to address them.
11. Your Website Has Keyword Cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization occurs when multiple pages on your site are targeting the same or similar keywords. This can confuse search engines about which page to rank for a given query, potentially resulting in lower rankings for all of the affected pages.
The Solution
To resolve keyword cannibalization:
- Conduct a content audit: Identify pages that are targeting the same keywords or have overlapping topics using tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Screaming Frog.
- Consolidate content: If two or more pages cover similar topics, merge them into one comprehensive page. This will reduce competition within your site and help consolidate the authority of the new, unified page.
- Use canonical tags: If consolidating pages isn’t feasible, use canonical tags to indicate which version of the page should be prioritized by search engines.
- Revise internal linking: Make sure your internal links guide search engines and users toward the preferred page for the targeted keyword.
- Adjust keyword targeting: Update some of the affected pages to target related but distinct keywords, reducing competition and expanding your reach.
Addressing keyword cannibalization helps ensure that your pages aren’t inadvertently competing with each other, allowing each one to rank more effectively.
12. Your Website’s Content Is Not Optimized for Target Keywords
Proper keyword optimization is crucial for helping search engines understand the content and context of your pages. If your content isn’t optimized for the right target keywords, your pages may not appear in relevant search results.
How Do I Check if My Website’s Content Is Optimized for Target Keywords?
To evaluate content optimization:
- Use SEO tools like SurferSEO, Yoast, or Clearscope to analyze your pages for target keyword usage. These tools can provide insights into keyword density, placement, and related keywords.
- Perform a manual check: Ensure your target keywords are present in key areas such as title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and the first 100 words of the content.
- Check keyword frequency and variation: While it’s important to use your main keyword, also include synonyms and related terms throughout the content to avoid keyword stuffing.
The Solution
To optimize your content for target keywords:
- Use keywords strategically: Incorporate your primary keyword in the title tag, headings (H1, H2), meta description, and within the content itself. Avoid overusing the keyword, as this can be seen as keyword stuffing.
- Leverage semantic keywords: Include related phrases and synonyms to give search engines a better understanding of your content’s context.
- Update outdated content: Refresh your content to include more recent information and optimize for current search trends. This can involve tweaking keywords or expanding content to cover more relevant subtopics.
- Optimize for search intent: Make sure the content aligns with what users are looking for when they search for your target keyword (informational, navigational, or transactional intent).
Improving keyword optimization will help search engines rank your content for the right queries, increasing your chances of appearing in search results.
13. Your Content Is Not Providing Value to Your Users
Content that fails to meet user needs or answer their questions won’t perform well in search rankings. If your content is thin, outdated, or lacks depth, search engines may not consider it valuable enough to rank.
The Solution
To make your content more valuable:
- Provide in-depth information: Make sure your content is comprehensive and addresses various aspects of the topic. This includes adding statistics, case studies, examples, or infographics that make your content more informative.
- Update your content regularly: Refresh older content to ensure it remains relevant and accurate. Adding recent developments or new insights can significantly improve its value.
- Focus on readability: Break up text with subheadings, bullet points, and short paragraphs. This makes your content easier to digest, which can improve user engagement metrics like time on page.
- Engage with multimedia elements: Add images, videos, or other multimedia content to make your page more interactive and engaging.
How Do I Check if My Content Is Providing Value?
To evaluate whether your content is valuable:
- Check user engagement metrics: Monitor metrics such as bounce rate, average time on page, and conversion rates using tools like Google Analytics.
- Look at user feedback: If users are leaving comments, asking questions, or sharing your content, it indicates that they find it valuable.
- Monitor social shares: High social engagement can suggest that your content resonates with your audience.
Enhancing the value of your content will lead to higher user satisfaction and improved search engine rankings.
14. Your Website Has Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content occurs when identical or very similar content appears on multiple pages of your website. This can confuse search engines and dilute the authority of the original content, leading to ranking difficulties.
How Do I Check if My Site Has Duplicate Content Issues?
To detect duplicate content:
- Use tools like Copyscape, Siteliner, or Screaming Frog to identify instances of duplicate content across your site.
- Manually compare content: Review pages that are targeting similar keywords or topics to see if the content overlaps.
- Check for syndication issues: If you syndicate content from other sites, ensure proper canonical tags are used to avoid duplicate content penalties.
The Solution
To resolve duplicate content issues:
- Use 301 redirects: Redirect duplicate pages to the preferred version to consolidate link equity and avoid confusion.
- Implement canonical tags: Indicate the preferred version of a page using canonical tags, telling search engines which page to prioritize.
- Rewrite duplicate content: Update and revise the content to make each page unique, focusing on providing different perspectives or additional insights.
- Avoid thin content: Combine similar content pieces into a more comprehensive page rather than having multiple, less valuable pages.
Addressing duplicate content issues ensures that search engines can identify the most relevant version of your content, improving your site’s ranking potential.
Google SEO Algorithm Changes and Penalties
Search engine algorithms are continually evolving to improve user experience and deliver the most relevant results. Consequently, SEO strategies need to adapt to these changes. Algorithm updates or penalties can impact your website’s rankings, often resulting in a significant drop in visibility.
15. You Are Affected by Google’s SEO Algorithm Changes
Google frequently updates its search algorithms to improve the quality of search results. These updates can affect rankings, causing some sites to gain visibility while others lose it. If your site experiences a sudden drop in traffic or rankings, it might be due to an algorithm change. Common algorithm updates focus on factors like content quality, backlinks, mobile usability, and page speed.
The Solution
To mitigate the impact of algorithm changes:
- Stay informed about algorithm updates: Follow SEO news and blogs such as Search Engine Journal, Moz, or Google’s Webmaster Blog to stay updated on the latest changes. Understanding how updates may impact your site will allow you to adjust strategies proactively.
- Conduct a site audit: Use tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Screaming Frog to identify areas where your site may not be complying with Google’s best practices. Pay attention to issues like content quality, backlink profile, site speed, and mobile usability.
- Improve content quality: Focus on creating high-quality, original, and informative content that satisfies user intent. Google’s updates often target thin or duplicate content, so providing value to readers should be a priority.
- Diversify traffic sources: Don’t rely solely on organic search traffic. Invest in other channels like social media, email marketing, and paid search to balance traffic sources.
- Monitor performance continuously: Use Google Analytics and Google Search Console to keep track of your site’s performance metrics. Watch for any sudden dips in traffic or changes in user behavior, which may indicate the need for adjustments.
16. You Have a Penalty From Google
Google penalties can occur when a site is found to be violating Google’s webmaster guidelines, either intentionally or unintentionally. Penalties can be manual (imposed by a human reviewer) or algorithmic (triggered automatically due to a breach in guidelines). A penalty can cause a dramatic drop in search rankings and organic traffic.
The Solution
To resolve Google penalties:
- Identify the type of penalty: Use Google Search Console to check for manual actions. If a manual penalty is applied, you’ll see a notification with details about the violation. For algorithmic penalties, a sudden drop in traffic may coincide with known algorithm updates.
- Review Google’s guidelines: Familiarize yourself with Google’s Webmaster Guidelines to understand what led to the penalty. Common reasons include spammy backlinks, thin content, keyword stuffing, or cloaking.
- Clean up your backlink profile: If the penalty is related to toxic backlinks, use tools like Ahrefs, Moz, or Majestic to identify and disavow spammy links. You can submit a disavow file to Google to inform them which links you want to exclude from consideration.
- Fix on-page issues: If the penalty is due to on-page issues, such as thin content or keyword stuffing, take steps to improve the quality of your content. Make it more comprehensive, original, and aligned with user intent.
- Submit a reconsideration request: If you’ve addressed a manual penalty, submit a reconsideration request through Google Search Console explaining the actions you’ve taken to resolve the issue.
- Monitor for improvements: After submitting a reconsideration request or resolving on-page issues, keep monitoring your site’s performance for any signs of recovery. Use tools like Google Analytics and Search Console to track progress.
Resolving penalties can be a time-consuming process, but addressing the underlying issues and adhering to best practices will ultimately improve your site’s long-term ranking stability.
How Do You Know if Your Content/Site Is Performing Well in the First Place?
To determine whether your content or site is performing well, you need to track various user engagement metrics that offer insights into how visitors interact with your site. These metrics help you assess the quality of user experience, content relevance, and the effectiveness of your SEO efforts. Monitoring engagement metrics is essential for making data-driven improvements to your website.
Some User Engagement Metrics to Track Include:
- Time on Page
The amount of time users spend on a particular page can indicate how engaging or valuable the content is. If visitors stay on the page longer, it suggests they are finding the content helpful. However, a low average time on page may imply that users are not finding the content useful, or they may be quickly exiting the page due to poor content quality or formatting. - Bounce Rate
Bounce rate measures the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page. A high bounce rate may suggest that the content is not meeting users’ expectations, or that there are technical issues, such as slow loading times or a lack of mobile-friendliness. While a high bounce rate is not always bad (e.g., if the page is a blog post that answers a specific question), it often indicates areas where user engagement can be improved. - Social Shares
The number of times your content is shared on social media platforms can serve as a signal of content quality and relevance. When users share your content, it implies that they find it valuable enough to recommend to others. More social shares can lead to increased traffic and may indirectly improve your rankings due to the enhanced visibility and potential backlinks. - Retention Rate
Retention rate indicates the percentage of visitors who return to your site over a specific period. High retention rates typically mean that your content is compelling enough to bring users back for more, which is an indication of user satisfaction and content effectiveness. Retention can be improved by regularly updating content, offering fresh insights, and maintaining a user-friendly website structure.
How Can You Track User Engagement Metrics?
To monitor and analyze user engagement metrics, there are several tools available that can provide comprehensive insights into your website’s performance. Here are some of the best ways to track user engagement metrics:
- Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a powerful and free tool for tracking a wide range of user engagement metrics, such as time on page, bounce rate, user sessions, and more. It allows you to set up goals and track conversions, providing a detailed view of how users interact with your content. You can use Google Analytics to segment data by source, device, or user behavior, giving you insights into specific areas where performance can be improved. - Google Search Console
While primarily used for monitoring site performance in search results, Google Search Console can also provide insights into user engagement metrics. It offers data on click-through rates (CTR), average position in search results, and the number of impressions your pages receive. You can identify pages with a high impression count but low CTR to optimize title tags and meta descriptions for better engagement. - Heatmap Tools (e.g., Hotjar, Crazy Egg)
Heatmap tools like Hotjar or Crazy Egg can help you understand user behavior by visualizing where users are clicking, how far they are scrolling, and which parts of your pages they are interacting with the most. This data can be used to optimize page layouts, improve call-to-action placement, and enhance overall user experience. - Social Media Analytics
If social shares are an important metric for your content strategy, social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn provide their own analytics tools to track the number of shares, likes, and comments your content receives. These insights can help you understand which types of content resonate best with your audience and guide future content creation efforts. - User Feedback and Surveys
Gathering direct user feedback through surveys, polls, or on-site feedback forms can provide valuable insights into user satisfaction. Tools like SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or Qualaroo can be used to collect feedback, helping you identify areas for improvement based on users’ opinions and experiences.
Is Your Optimized Page Still Not Ranking Well?
Your optimized page still not ranking well despite following every step in our guide? It may be time to call in the experts for a professional touch. While do-it-yourself SEO troubleshooting is a good start for optimizing your website, there comes a point when expert guidance becomes essential.
Pro Real Tech, a leading SEO company, offers comprehensive technical audits and tailored solutions for businesses that want to improve their search rankings. We go beyond just optimizing your site—we focus on achieving long-term success through a holistic local SEO strategy that aligns with your business goals.
Don’t let ranking issues hold back your online growth. Contact Pro Real Tech today to get a comprehensive SEO strategy designed to boost your site’s rankings and drive more organic traffic!





